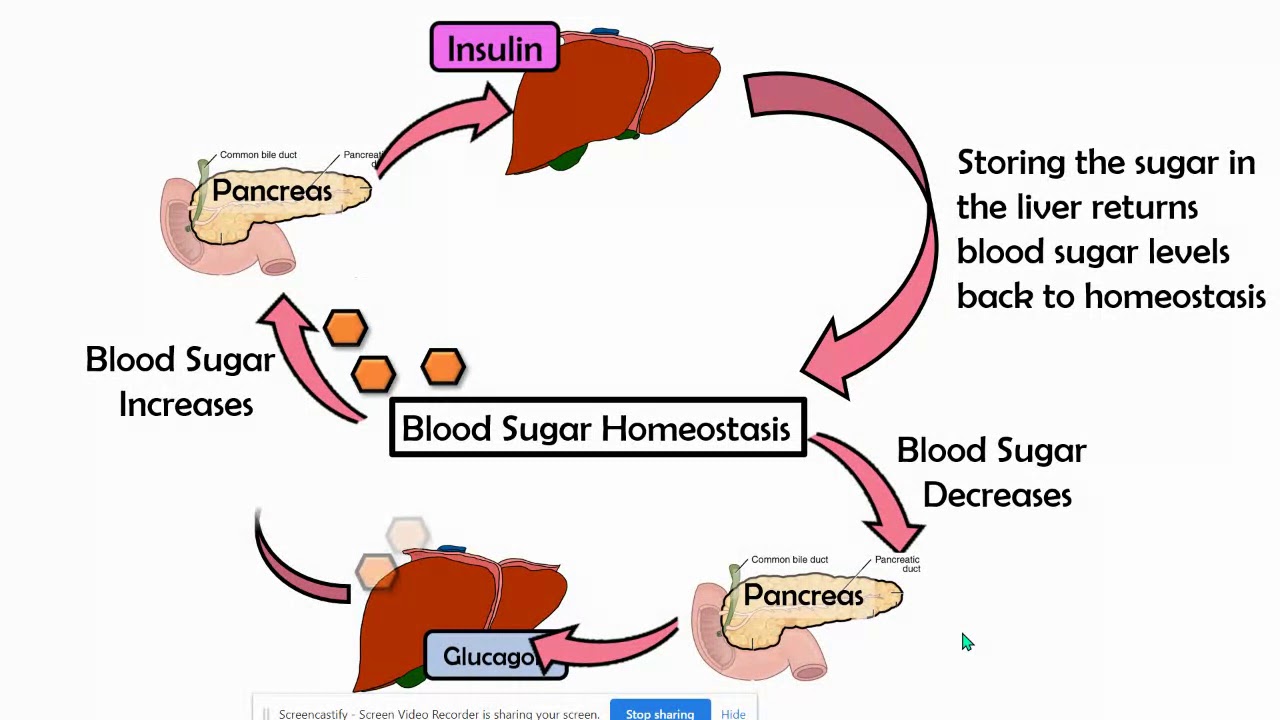
Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar . After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism.
from www.youtube.com
homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in.
Blood Sugar Negative Feedback Loop YouTube
Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar.
From quizlet.com
Blood Glucose Negative Feedback Loop Diagram Quizlet Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. After a meal, the small intestine. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.shalom-education.com
Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration GCSE Biology Revision Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. . Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From books.lib.uoguelph.ca
Concepts of Hormone Secretion Human Physiology Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar When blood sugar rises, receptors in. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. . Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT AP Biology Unit Four Maintaining Homeostasis PowerPoint Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. identify the five. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Homeostasis homeo the same stasisstable, stationary, static Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.researchgate.net
Standard onelayer feedforward neural network (left) and recurrent Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.studocu.com
Neg feedback loop insulin and glucagon Name Rebecca Randle Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. the negative feedback diagram. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.elucidate.org.au
Blood Glucose Feedback Loops What are the negative feedback loops Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a.. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.scientistcindy.com
Homeostasis Physio SCIENTIST CINDY Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. the control of. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.biologycorner.com
Feedback Loops Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From mavink.com
Glucose Homeostasis Feedback Loop Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what would happen if secretion of a body chemical controlled by a. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From bio.libretexts.org
Feedback Loops Glucose and Glucagon Biology LibreTexts Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain what. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From biologydictionary.net
Feedback Mechanism The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. an important example of negative feedback is the control of. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.researchgate.net
Causal loop diagram for the regulation of blood glucose levels Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. in this explainer, we will learn how to describe the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon as an example of. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. homeostasis is generally maintained by. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From userdatarheumatics.z21.web.core.windows.net
Blood Glucose Levels Negative Feedback Loop Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus,. an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.researchgate.net
Regulation of blood glucose occurs through insulin. Regulation of blood Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From socratic.org
What secretion regulates the blood sugar level? Socratic Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar an important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. When blood sugar rises, receptors in. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. identify the five components of a negative feedback loop and explain. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.
From www.chegg.com
Solved In the negative feedback mechanism regulating blood Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway. the negative feedback diagram provides a useful tool for global evaluation of the ability of the organism to blunt the increase of blood glucose. the control of blood sugar (glucose) by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback. Negative Feedback Loop Example Blood Sugar.